Serotonin: The Mood Regulator
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter found in the gut and the brain. There are serotonin receptors in the brain, but the majority of them are found in the gut, where it impacts numerous biological processes such as, digestion, appetite, metabolism, mood and memory. Serotonin plays a role in appetite regulation, intestinal motility. and inflammation. It produces more of the chemical that helps eliminate foods that irritate the digestive system quickly. Serotonin is also is necessary for mood stabilization, getting good sleep, dreaming, and visualization. Low serotonin levels are associated with constipation, depression, anxiety, trouble sleeping, obsessive thinking, and addiction to alcohol or drugs. Shifts in serotonins levels and emotions (negative to positive) are normal and expected, but chronically low levels can have a major negative impact on our health. Negative emotional states cause stress on the body and activates the immune response leading to increased chronic low-grade inflammation, higher risk for mental health issues, and weakened immune function. Focus on a healthy diet, exercise, mindfulness, and self-care to maintain adequate serotonin levels.

Functions of Serotonin
Serotonin (5-HT) is a neurotransmitter and endorphin that plays key roles in numerous biological processes. Serotonin receptors are found in the brain and the gut. It is crucial to maintain adequate levels. In the brain, serotonin regulates motor function, cardiovascular function, energy balance, pain perception and appetite. In the gut, it regulates hormonal, endocrine, autocrine, and paracrine actions. Serotonin is released during physical activity as well. Exercise is very important for getting an adequate amount of serotonin. It gives us a rush of feel good chemicals, boosts energy levels, keeps us motivated, and leaves us with an overall positive outlook on life. Proper serotonin levels simply help us feel good and normal.
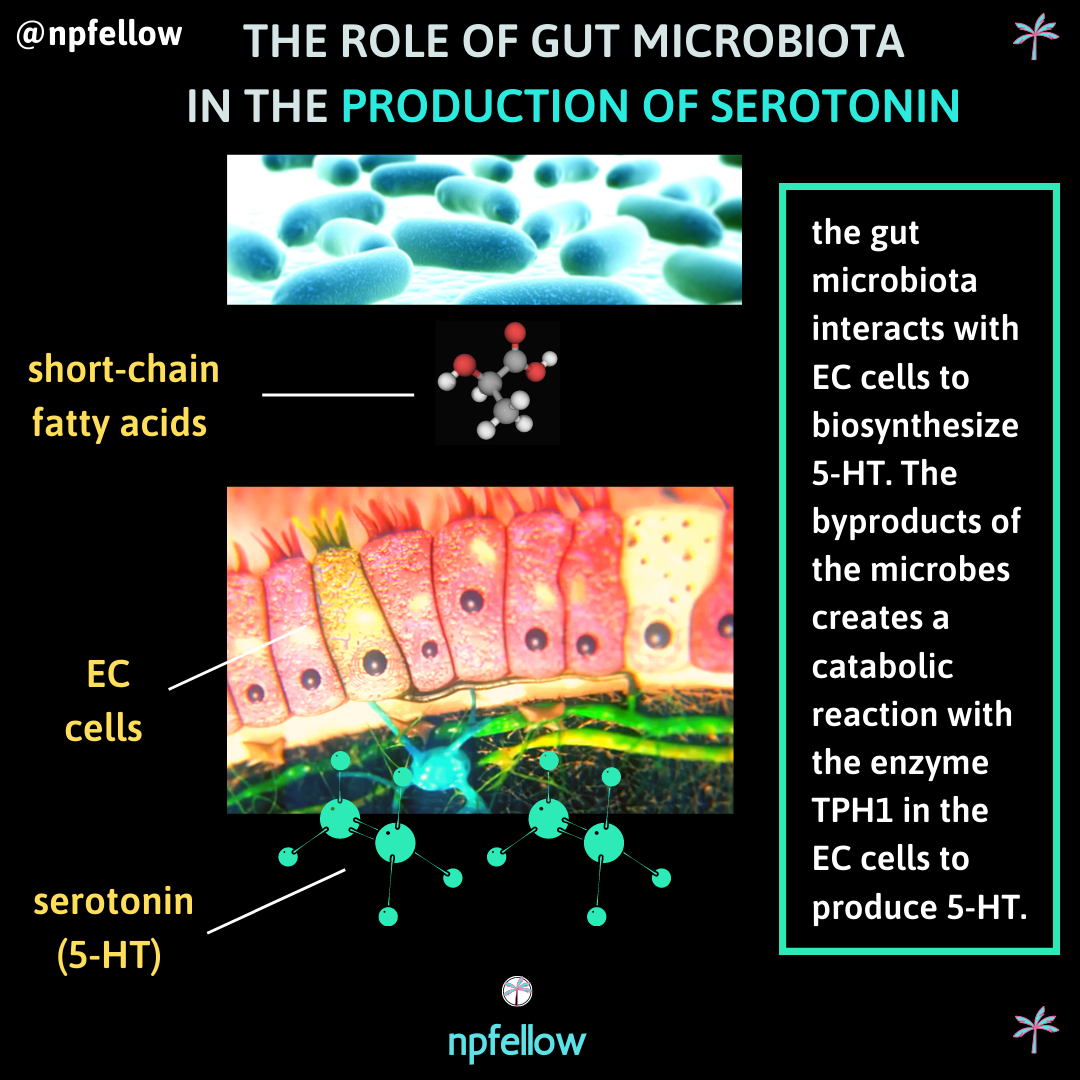
The Gut Micrbiome's Role in Serotonin Production
We know that the gut microbiota regulates inflammation and maintains the intestinal wall and mucosal lining, which prevents common colds, chronic inflammatory diseases, cancer, obesity and leaky gut. The gut microbiota also regulates the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter and “feel good” hormone, serotonin (5-HT). 95% of the serotonin in the human body is produced in the intestine, starting with the indigenous spore-forming bacteria in the gut. The byproducts of the gut microbiome interact with an enzyme in the enterochromaffin (EC) cells in the intestine to synthesize and release serotonin to the stomach lining and circulating platelets. Not only does serotonin regulate mood, but also regulates digestion. It plays a key role in appetite regulation, intestinal motility, and inflammation. Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is crucial for adequate serotonin production.

Natural Ways to Boost Serotonin
Natural ways to maintain adequate serotonin levels can be practiced everyday. Exercise is crucial for boosting not only serotonin, but all endorphins. It has similar mind-body benefits to meditation. “Runner’s high” is linked to increased endorphin production. Exercise increases self-esteem. gives us a sense of accomplishment, boosts energy levels, keeps us in an inspired state of mind. eating a healthy diet is also crucial to increase serotonin. Adequate amounts of protein is essential for serotonin production. Eat amino-rich foods like wild salmon, seeds, nuts, beans, and sprouted grains; veggies like broccoli, spinach and cauliflower; and antioxidant-rich foods like leafy greens, citrus, berries, sweet potato and squash to prevent free radical damage. Sunlight regulates the release of serotonin and melatonin which regulates our circadian rhythm. Taking in 20 minutes of sunlight in nature is crucial for our mood and allows our skin to absorb UV rays to produce vitamin D. Regular exercise and sunlight are the top two ways to give ourselves an instant mood boost.
Thank you for reading this post.
